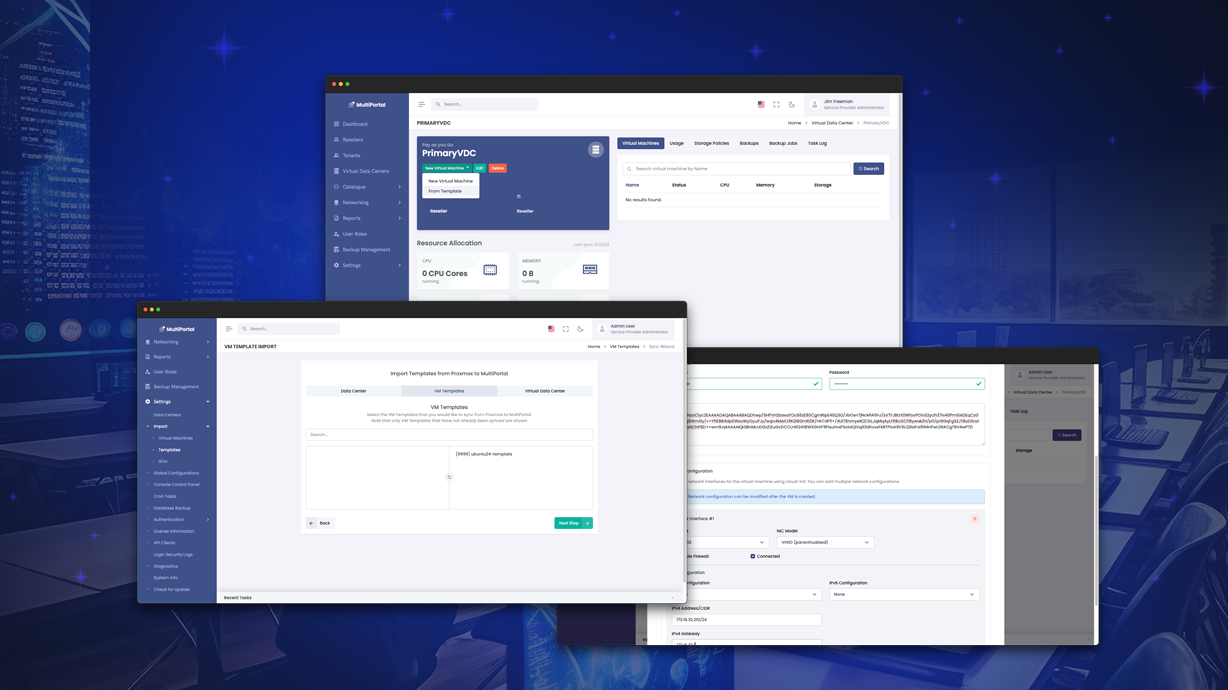
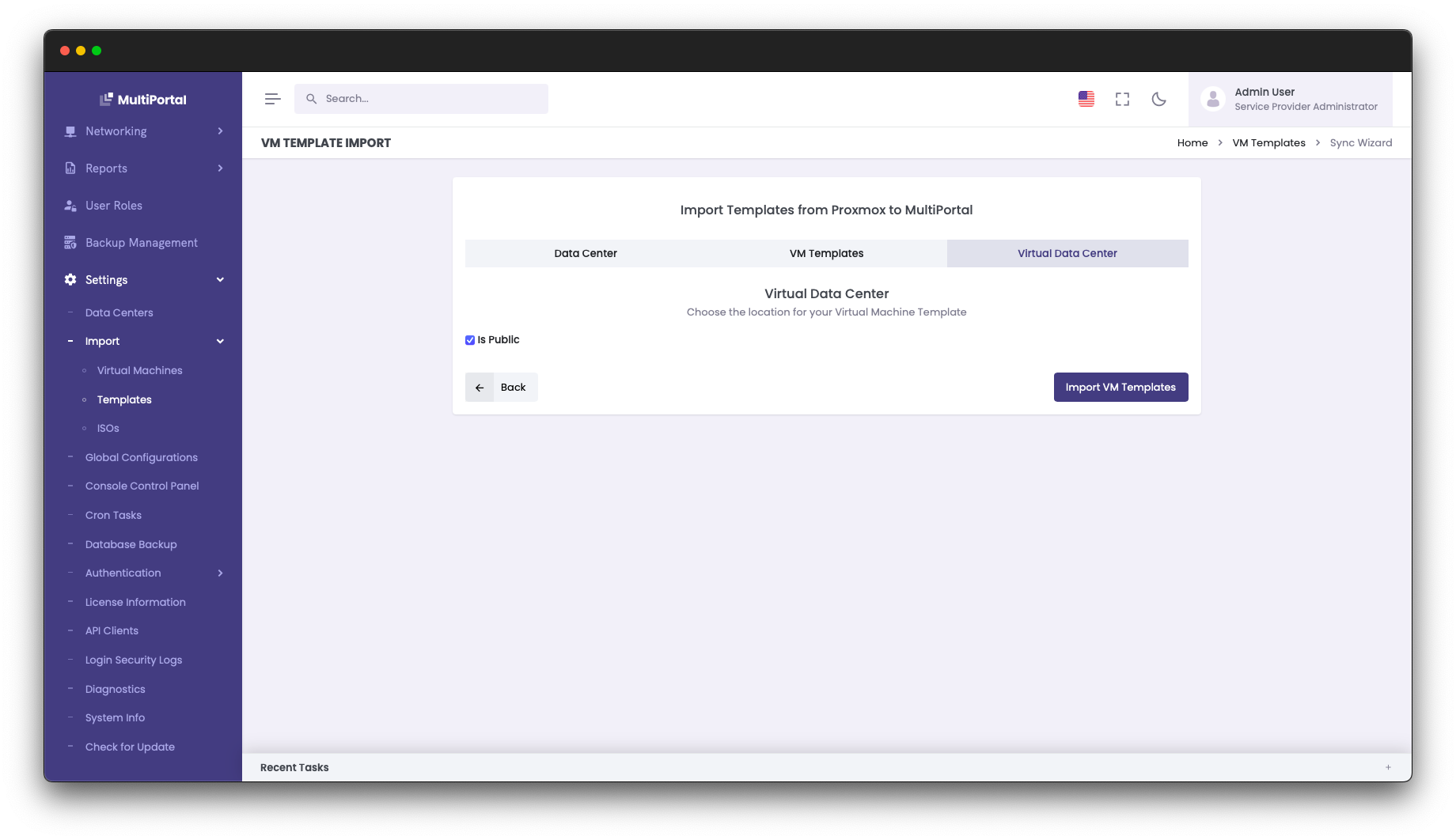
When setting up MultiPortal for your tenants, it’s often a good idea to pre-create templates for popular operating systems and applications to speed up provisioning and deployment.
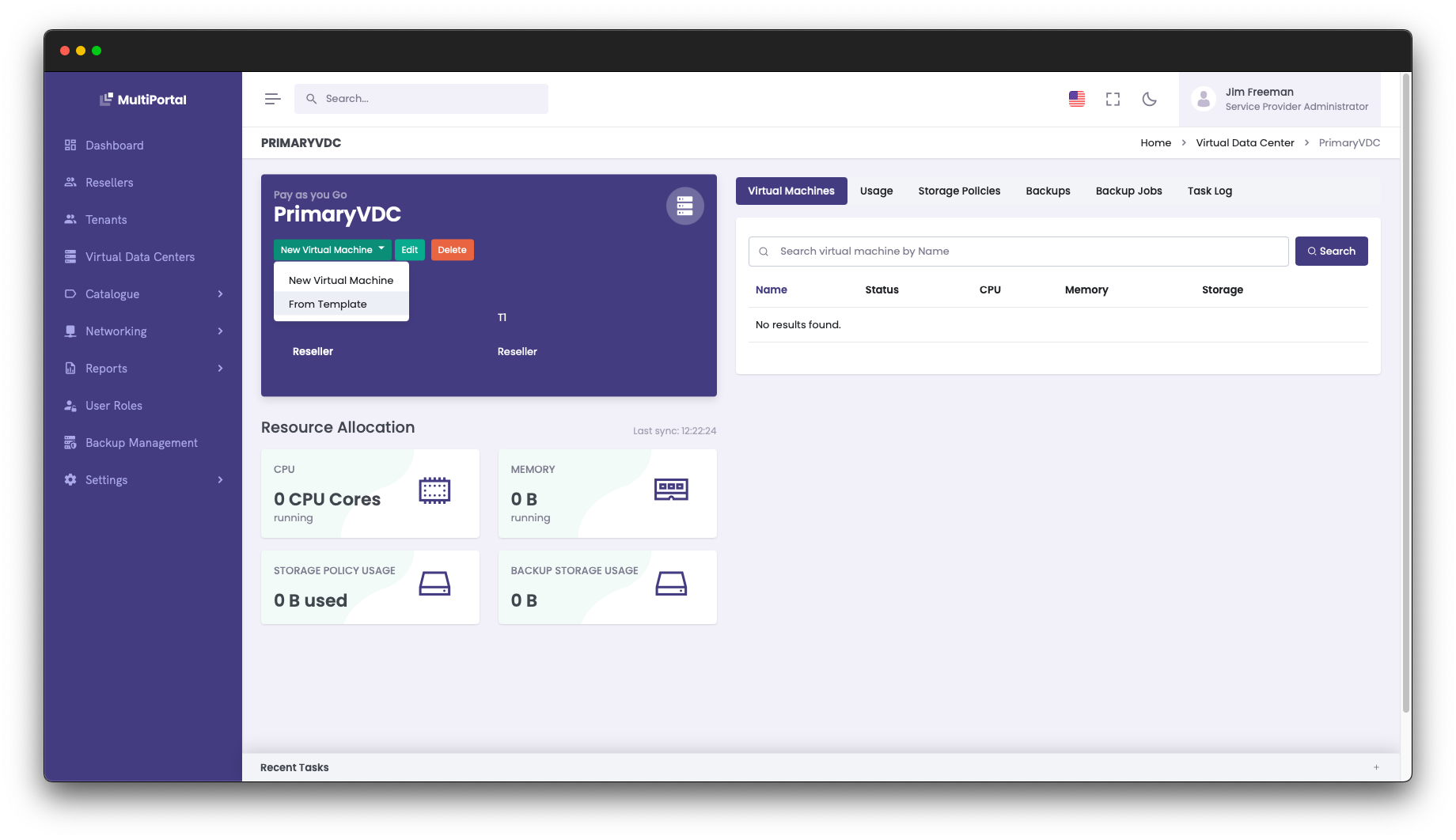
Within a MultiPortal Virtual Data Center, your end users have the ability to build VMs from scratch or deploy from the aforementioned template. In this blog post, I will show you how you can configure this in Proxmox so it can be imported into MultiPortal. This, combined with our improved CloudInit support, creates a great experience for your end users.
To get started, we are going to use a pre-created Cloud Image from Ubuntu that can be found on Ubuntu’s Cloud Images repository. Many popular operating systems have their own repositories for such images, including Alma Linux, Debian, Oracle Linux and many more. Make sure you download your desired version and correct architecture (amd64, arm64, etc.) for your environment.
I will be downloading the latest LTS version of Ubuntu as of this document being written, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat). Download this to one of your Proxmox nodes:
root@proxmox20:~# wget https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/noble/current/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img
As the default download size is quite small, resize this to an appropriate base size for your own environment (10GB in my example):
root@proxmox20:~# qemu-img resize noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img 10G
Now we have our disk image downloaded, we will create a VM in Proxmox that we will eventually convert to a template.
qm create 9999 --name "ubuntu24-template" --ostype l26 --memory 2048 --agent 1 --bios ovmf --machine q35 --scsihw virtio-scsi-single --efidisk0 <DataStore_Name>:0,format=qcow2 --sockets 1 --cores 1
Many aspects of this can be changed based on your own requirements, for example the VM specification, machine/BIOS types. Check out the Proxmox documentation for full details. Also, be sure to replace <DataStore_Name> with the name of a datastore in your own environment that can be used for disk image storage.
Note: All of these examples will be using file-based (qcow2) images – if you are using block-based storage (eg. LVM Thin, which is the Proxmox local storage default), you may need to change the format to “raw” instead.
Next, we will import our previously downloaded Cloud Image from Ubuntu, and assign it to the virtual machine:
qm set 9999 --scsi0 <DataStore_Name>:0,import-from=/<PATH_TO>/noble-server-cloudimg-amd64.img,format=qcow2,iothread=1
Remember to replace <DataStore_Name> with the name of a datastore in your own environment that can be used for disk image storage and the correct path to the downloaded Cloud Image.
Now we will set our newly imported disk image to be the primary boot disk:
qm set 9999 --boot order=scsi0
We will now add a CloudInit disk to allow us to define our own run-once script, as well as allowing MultiPortal to automatically set additional configurations, such as networks, SSH keys and authentication credentials.
qm set 9999 --scsi1 <DataStore_Name>:cloudinit
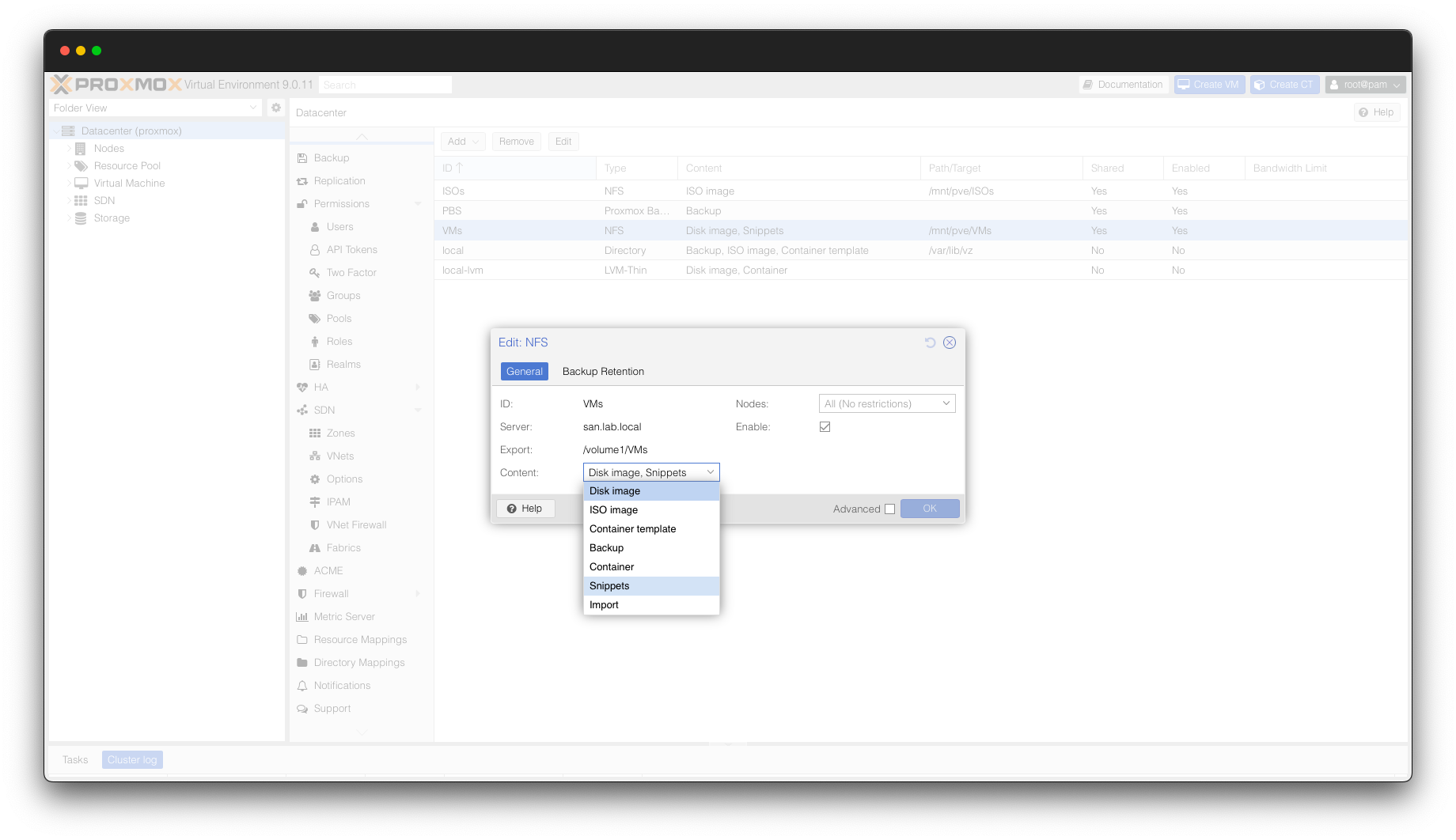
Next, we will ensure we have a Datastore that is configured for snippets – this could be the same shared or local datastore that you are using for your virtual machine storage. In Proxmox, go to your DataCenter, click “Storage” and ensure there is a Datastore that supports the “snippets” content type.